How they work...
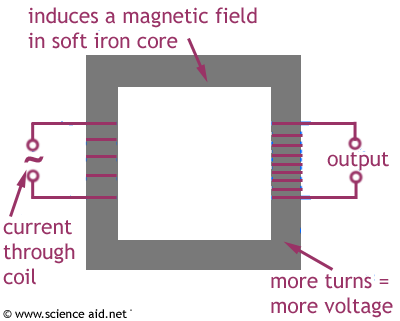
A wire carrying a current is wrapped round one side of the transformer, another wire is wrapped round the other. There will be the same amount of power on both sides, but one will have a higher voltage and lower current the other a lower voltage and a higher current.
The transformer is made of iron, this is because it is a soft metal and can be turned on and off as a magnet (it is a magnetically soft material): the current from the first wire induces a magnetic field in the transformer, this then induces a current in the second wire.
More coils causes more higher voltage (and lower current). So if the second side has more turns of wire wrapped round the transformer it will step the voltage up (step up transformer.) If the second side has less turns, the voltage will be stepped down and current increased (step down transformer).
 |
If your having trouble getting to grips with this (it is very hard!), the animation at the bottom of this page may help... http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/gcsebitesize/science/edexcel/generation_transmission_electricity/transmitting_electricityrev2.shtml
No comments:
Post a Comment